Voltage measurement of a 12V car battery
Measuring the voltage of a 12-volt car battery is a simple process performed using a multimeter. Here is a guide on how to measure your car battery voltage:
Needed tools:
- A digital multimeter that can measure direct voltage (DC).
Steps to measure voltage:
1. Preparation of multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure direct voltage (DC). This is often indicated by a symbol that resembles a solid line with three dashed lines underneath, or simply by the letter "V" with a straight line sign above it.
- Choose a voltage range that is above 12 volts to ensure the measurement is within the multimeter's range. Many multimeters have an automatic range that is also suitable.
2. Carry out measurement:
- Turn on the multimeter.
- Connect the red measuring cable of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery and the black cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
- Be sure to make a good connection to get accurate readings.
3. Reading the voltage:
- Read the value on the multimeter. A fully charged one
A 12-volt car battery should have a voltage of between 12.6 when idle
and display 12.8 volts. Values below 12.4 volts indicate that
the battery needs to be charged. Values well below 12 volts mean
that the battery is discharged or defective.
Tips for accurate measurements:
- Carry out the measurement while the vehicle is switched off and no consumers (such as lights, radio, etc.) are switched on.
- If the battery has recently been charged or the vehicle has been driven, wait a few minutes for the voltage to stabilize before taking the measurement.
Battery voltage monitoring with a HOOTS battery computer:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
Important instructions:
- The voltage alone does not always provide information about the overall condition of the battery. A battery may have normal resting voltage but not provide enough current to turn the starter. Further testing, such as a stress test, may be required to fully assess the health of the battery.
- Safety should always be a priority. Make sure you use the multimeter correctly and follow all manufacturer safety instructions.
Voltage measurement of a 12V car battery
Measuring the voltage of a 12-volt car battery is a simple process performed using a multimeter. Here is a guide on how to measure your car battery voltage:
Needed tools:
- A digital multimeter that can measure direct voltage (DC).
Steps to measure voltage:
1. Preparation of multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to measure direct voltage (DC). This is often indicated by a symbol that resembles a solid line with three dashed lines underneath, or simply by the letter "V" with a straight line sign above it.
- Choose a voltage range that is above 12 volts to ensure the measurement is within the multimeter's range. Many multimeters have an automatic range that is also suitable.
2. Carry out measurement:
- Turn on the multimeter.
- Connect the red measuring cable of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery and the black cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
- Be sure to make a good connection to get accurate readings.
3. Reading the voltage:
- Read the value on the multimeter. A fully charged one
A 12-volt car battery should have a voltage of between 12.6 when idle
and display 12.8 volts. Values below 12.4 volts indicate that
the battery needs to be charged. Values well below 12 volts mean
that the battery is discharged or defective.
Tips for accurate measurements:
- Carry out the measurement while the vehicle is switched off and no consumers (such as lights, radio, etc.) are switched on.
- If the battery has recently been charged or the vehicle has been driven, wait a few minutes for the voltage to stabilize before taking the measurement.
Battery voltage monitoring with a HOOTS battery computer:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
Important instructions:
- The voltage alone does not always provide information about the overall condition of the battery. A battery may have normal resting voltage but not provide enough current to turn the starter. Further testing, such as a stress test, may be required to fully assess the health of the battery.
- Safety should always be a priority. Make sure you use the multimeter correctly and follow all manufacturer safety instructions.

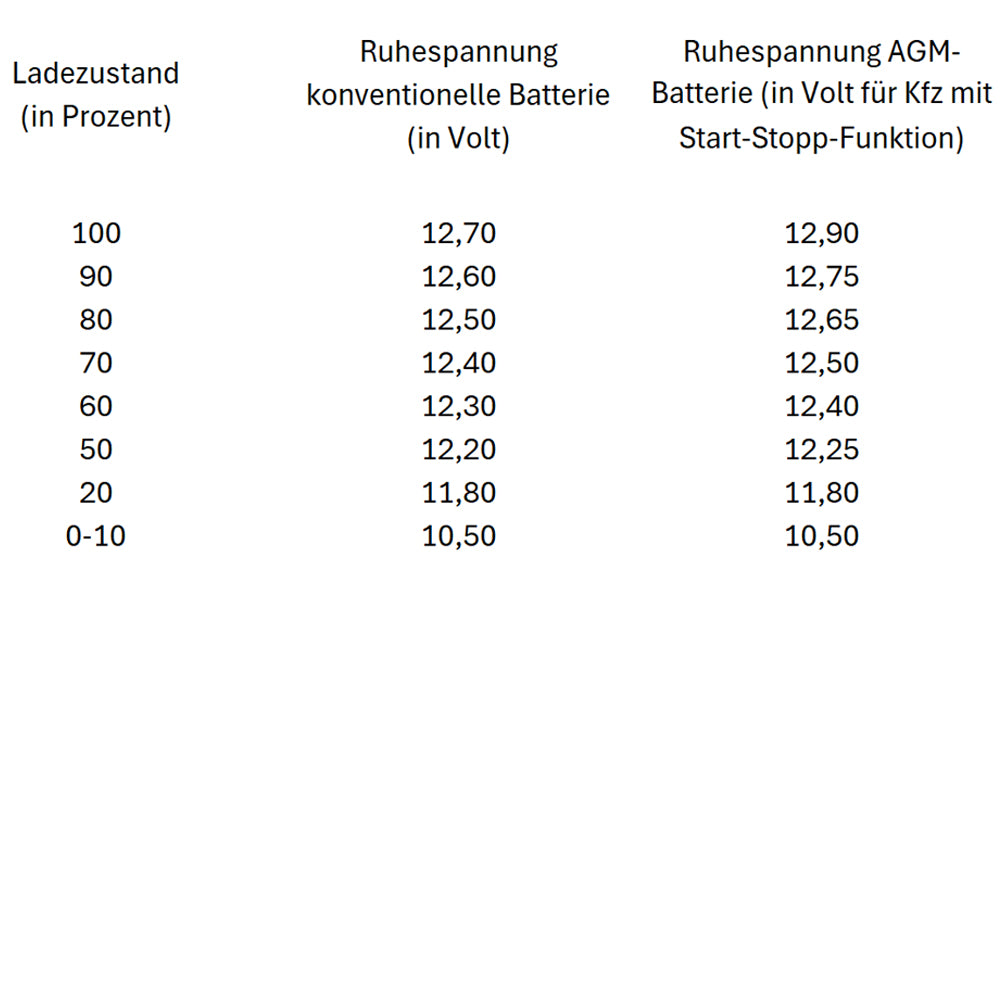
Wie viel Volt hat eine Autobatterie?
Here you will find a table that shows the typical charging voltage values for a conventional 12-volt car battery under various operating conditions. The charging voltage can vary depending on the condition of the battery, the temperature and the charger.
What do I have to consider when getting jump-start help?
When jump-starting a vehicle with a dead battery, there are several important steps and safety precautions that must be followed to avoid vehicle damage or injury. Here are the basic guidelines:
Safety precautions
- Check the battery voltage: Make sure both vehicles have the same voltage (usually 12 volts).
- Wear protective clothing: Use safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from sparks or leaking battery acid.
- No smoking: Do not smoke near the batteries and avoid open flames or sparks.
- Damaged Batteries: Do not perform a jump start if any of the batteries are obviously damaged, leaking, or frozen.
- Turn off electronics: Turn off all electronic devices in both vehicles before jump starting.
Connecting the jumper cables
- Position the vehicles: Place the vehicles as close to each other as possible without touching each other. Both vehicles should be turned off.
- Connecting the Positive Terminals: Connect one end of the red jumper cable to the positive (+) terminal of the discharged battery and the other end to the positive terminal of the donor battery.
- Connecting the Negative Terminals: Connect one end of the black jumper cable to the negative (-) terminal of the donor battery. Connect the other end of the black cable to a bare metal part of the vehicle with the discharged battery, far away from the battery to avoid sparking.
- Final check: Check that the cables are secure and do not come into contact with moving parts or heat sources.
Starting the vehicle
- Start the donor vehicle: Run the engine of the donor vehicle for a few minutes to slightly charge the discharged battery.
- Start the vehicle with the discharged battery: After a few minutes, try starting the vehicle with the discharged battery. If it doesn't start immediately, wait a few more minutes and try again.
- Disconnecting the Cables: Once the vehicle is started, disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse order in which they were installed. When doing so, avoid that the cable ends come into contact with each other or with the vehicle.
After the jump start
- Run the engine of the vehicle with the previously discharged battery for a while to further charge the battery.
- It may be helpful to take the vehicle on a longer trip or to fully charge the battery using a charger.
Important to note
- Modern vehicles with extensive electronics can react sensitively to voltage spikes. Consult your vehicle's manual for specific jump starting instructions or if any special precautions are required.
Wie viel Volt hat eine Autobatterie?
Here you will find a table that shows the typical charging voltage values for a conventional 12-volt car battery under various operating conditions. The charging voltage can vary depending on the condition of the battery, the temperature and the charger.
What do I have to consider when getting jump-start help?
When jump-starting a vehicle with a dead battery, there are several important steps and safety precautions that must be followed to avoid vehicle damage or injury. Here are the basic guidelines:
Safety precautions
- Check the battery voltage: Make sure both vehicles have the same voltage (usually 12 volts).
- Wear protective clothing: Use safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from sparks or leaking battery acid.
- No smoking: Do not smoke near the batteries and avoid open flames or sparks.
- Damaged Batteries: Do not perform a jump start if any of the batteries are obviously damaged, leaking, or frozen.
- Turn off electronics: Turn off all electronic devices in both vehicles before jump starting.
Connecting the jumper cables
- Position the vehicles: Place the vehicles as close to each other as possible without touching each other. Both vehicles should be turned off.
- Connecting the Positive Terminals: Connect one end of the red jumper cable to the positive (+) terminal of the discharged battery and the other end to the positive terminal of the donor battery.
- Connecting the Negative Terminals: Connect one end of the black jumper cable to the negative (-) terminal of the donor battery. Connect the other end of the black cable to a bare metal part of the vehicle with the discharged battery, far away from the battery to avoid sparking.
- Final check: Check that the cables are secure and do not come into contact with moving parts or heat sources.
Starting the vehicle
- Start the donor vehicle: Run the engine of the donor vehicle for a few minutes to slightly charge the discharged battery.
- Start the vehicle with the discharged battery: After a few minutes, try starting the vehicle with the discharged battery. If it doesn't start immediately, wait a few more minutes and try again.
- Disconnecting the Cables: Once the vehicle is started, disconnect the jumper cables in the reverse order in which they were installed. When doing so, avoid that the cable ends come into contact with each other or with the vehicle.
After the jump start
- Run the engine of the vehicle with the previously discharged battery for a while to further charge the battery.
- It may be helpful to take the vehicle on a longer trip or to fully charge the battery using a charger.
Important to note
- Modern vehicles with extensive electronics can react sensitively to voltage spikes. Consult your vehicle's manual for specific jump starting instructions or if any special precautions are required.

Product
How to check the charge level of a vehicle battery?
What voltage is normal for a 12 volt car battery?
A normal voltage for a fully charged 12-volt car battery at rest (that is, the vehicle is off and the battery is not under load) is about 12.6 volts or slightly higher. The exact voltage may vary depending on the specific condition and age of the battery, but here are some general guidelines:
- 12.6 volts or higher: The battery is considered fully charged.
- 12.4 volts: The battery is approximately 75% charged.
- 12.2 volts: The battery is approximately 50% charged.
- 12.0 volts: The battery is approximately 25% charged.
- Below 12.0 volts: The battery is considered discharged and may need to be charged or replaced, especially if it is significantly below this value.
When the engine is running and the charging system (alternator) is functioning correctly, the voltage at the battery terminals can be between approximately 13.7 and 14.7 volts. This voltage is necessary to charge the battery while the vehicle is operating and to power the vehicle's electrical systems.
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
It is important to note that voltage values may vary slightly depending on the condition of the battery, the temperature and how long the vehicle has been sitting. A measurement immediately after switching off the vehicle may be slightly higher due to the surface charge of the battery. It is recommended to test the battery after several hours of rest for an accurate measurement.
How do I measure the voltage in volts of a 12V car battery?
Measuring the battery voltage of a vehicle battery is a simple process performed using a multimeter. A multimeter is a device used to measure voltage, current and resistance. To measure the battery voltage, you only need the voltage measurement function. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Step 1: Preparation
- Make sure the vehicle is off: Before you begin, make sure the vehicle is turned off. This includes the engine, lights, radio, and other electronic devices that may use power.
- Set up your multimeter: Set your multimeter to the direct voltage (DCV) setting. For a vehicle battery that typically has a voltage rating of 12 volts, choose a measurement range that can cover 12 volts, typically the 20 volt setting on most multimeters.
Step 2: Connecting the multimeter
- Connect test leads: Connect the red test lead (positive) to the positive (+) pole of the battery and the black test lead (negative) to the negative (-) pole of the battery.
Step 3: Voltage measurement
- Read the measurement: Look at the display of your multimeter. A healthy, fully charged vehicle battery should display a voltage of approximately 12.6 volts when the vehicle is turned off and there is no load on the battery.
- Interpreting voltage values:
More tips
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Checking the charging system: You can also check the operation of the charging system by measuring the battery voltage with the engine running. The voltage should rise to around 13.7 to 14.7 volts, indicating that the charging system is working and charging the battery.
- Safety: Be sure to take safety precautions to avoid electrical shock or short circuit. Avoid touching metal parts of the test leads or battery terminals with your hands.
- Regular Check: It is a good idea to check the battery voltage regularly to ensure the battery is in good condition and to avoid any surprises, especially before long trips or in extreme weather conditions.
By regularly checking your battery voltage, you can effectively monitor the health of your vehicle battery and take steps to ensure your vehicle starts reliably.
How do I measure the current in amps of a 12V car battery?
Measuring the current (in amps) of a 12-volt car battery requires a multimeter or a special clamp-on ammeter suitable for DC measurements. For general current measurements, such as the vehicle's quiescent current consumption, you can use a traditional multimeter. However, for measuring the cranking current that occurs when the engine is started, a clamp-on ammeter is safer and more practical due to the high current, which is well beyond the measuring range of most commercially available multimeters.
Measuring the quiescent current with a multimeter:
- Make sure the multimeter is sufficient: Check that your multimeter can measure direct current (DC) up to at least 10 amps. This should be sufficient for the quiescent current measurement.
- Preparation: Switch off all consumers in the vehicle and wait about 15 minutes for all systems to go to sleep.
- Setting the Multimeter: Set the multimeter to the ampere (A) measurement range for direct current (DC).
- Connection: Disconnect the negative cable (usually black) from the battery. Connect the red measuring cable of the multimeter to the negative terminal of the battery and the black measuring cable to the disconnected negative cable of the vehicle.
- Measurement: Turn on the multimeter. The value displayed corresponds to the quiescent current drawn by the battery.
Measuring the starting current with a clamp ammeter:
To measure high currents, such as those that occur when starting the motor, you need a clamp-on ammeter that is designed for high DC currents.
- Setting the clamp-on ammeter: Set the clamp-on ammeter for DC current measurement.
- Measurement: Use the ammeter's clamps to wrap around one of the battery cables (preferably the positive cable). Be sure to wrap only one wire to get an accurate measurement.
- Starting the Engine: While someone is starting the engine, observe the maximum current value displayed on the clamp-on ammeter. This value is the starting current supplied by the battery.
Monitoring battery voltage with a HOOTS battery sensor:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
General tips:
- Regular maintenance: Check the condition of the batteries regularly, especially before long journeys.
- Keep clean: Keep the battery surface clean and dry to avoid self-discharge due to moisture.
- Secure connections: Ensure connections are tight and free of corrosion to ensure optimal performance.
By regularly checking and maintaining batteries, you can extend the life of your truck starter battery and ensure that your vehicle starts reliably.
Important safety instructions:
- To avoid damage to the device or injury, make sure your meter is rated for the range of current you are measuring.
- Care must be taken when working on the vehicle battery to avoid short circuits and sparks.
- Wear appropriate protective equipment, especially when working near vehicle batteries.
These methods allow safe and effective measurement of the current supplied by a 12 volt car battery, both quiescent current and cranking current.
How do you find a silent consumer in a car or truck?
Finding a silent load (also called a parasitic discharge) in a car or truck requires patience and a systematic approach. This step-by-step guide will help you identify the hidden power consumer:
1. Necessary tools
- A multimeter that can be set to the current measurement range (amps).
- The vehicle owner's manual to identify the various circuits and their fuses.
2. Preparation
- Make sure all consumers are turned off: lights, radio, etc.
- Switch off the ignition and remove the key.
- Wait approximately 15-30 minutes to allow all vehicle systems to enter sleep mode.
3. Check fuses
- Open the fuse box(es). There is often more than one in vehicles.
- Note the location and purpose of each fuse according to the manual.
4. Measuring the quiescent current
A battery monitor or voltage meter from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Switch your multimeter to the current measurement range (amps).
- Disconnect the negative battery cable.
- Connect the multimeter between the negative battery terminal and the disconnected cable. The multimeter now measures the total current drawn from the battery.
5. Identification of the silent consumer
- Watch the current measurement. A normal quiescent current is often in the range of 20-50 milliamperes (mA). Values above this indicate a silent consumer.
- Pull one fuse at a time and see if power consumption drops significantly. This will help you identify the circuit that contains the silent load.
- If power consumption drops after a particular fuse is pulled, check your manual to see which components are protected by that fuse.
6. Confinement and repair
- Once you have identified the problematic circuit, you need to examine the individual components of that circuit to find the exact load. This can be time consuming, especially if the circle has many components.
- Check these components for defects, loose connections, or other signs of problems.
7. Get specialist help
- If you cannot find the silent consumer or are unsure how to proceed, it is advisable to seek professional help. A professional has the experience and specialized diagnostic tools to solve such problems efficiently.
Tips
- Be careful not to lose any electronic settings (e.g. radio station or time) during the test. A memory saver can help preserve these settings.
- Be careful when handling electrical components to avoid damage or injury.
This systematic check allows you to identify the silent consumer and take appropriate measures to resolve the problem.
How do I check the condition of a 24 volt truck starter battery?
Checking the health of a 24-volt truck starter battery is essentially similar to checking a 12-volt car battery, but takes into account the specific requirements and configurations common to 24-volt systems. Many trucks use two 12-volt batteries connected in series to achieve the 24-volt system. Here's how you can check the health of such a battery:
1. Visual inspection
- Check the batteries for obvious damage: This includes cracks in the case, bulges, or fluid leaks.
- Check connections: Make sure battery terminals are clean, tight, and free of corrosion.
2. Voltage test
- Tools needed: A multimeter set to direct voltage (DC).
- Procedure: Measure the voltage across the battery terminals. With two 12-volt batteries connected in series, measure the voltage across the two outer terminals of the battery configuration to get a total voltage of 24 volts.
3. Load test (load test)
- Tool: A battery load tester specifically for 24 volt systems.
- How to: A load test tests the battery's ability to hold a specified load for a specified period of time without falling below a critical voltage. Follow the instructions for your specific stress tester.
4. Specific gravity check (for maintenance batteries)
- Tool: A hydrometer.
- Procedure: Check the specific gravity of the battery acid in each cell section. A uniformly high specific gravity across all cells indicates good condition. Differences between cells may indicate a problem.
5. Checking the charging system
- Measure the voltage on the battery system while the engine is running. The voltage should be between 27 and 28.8 volts, which indicates that the charging system is working correctly and charging the batteries.
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
General tips:
- Regular maintenance: Check the condition of the batteries regularly, especially before long journeys.
- Keep clean: Keep the battery surface clean and dry to avoid self-discharge due to moisture.
- Secure connections: Ensure connections are tight and free of corrosion to ensure optimal performance.
By regularly checking and maintaining batteries, you can extend the life of your truck starter battery and ensure that your vehicle starts reliably.
How can I test whether a 12V car battery is still OK?
To test whether a car battery is still OK, you can use various methods. Some of the most common and effective methods are measuring voltage with a multimeter, load testing (also known as cold crank testing), and checking battery health with a battery tester. Here are the steps for each method:
1. Measure voltage with a multimeter
- Preparation: Make sure that all electrical consumers in the car are switched off and the vehicle is not running.
- Set multimeter: Set your multimeter to measure direct voltage (DC) and select a range that is above 12 volts.
- Measurement: Connect the red cable of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery and the black cable to the negative (-) terminal. A healthy battery should read about 12.6 volts when idle.
- Interpretation: Values above 12.6 volts indicate a fully charged battery, while values below 12.0 volts indicate that the battery is weak or discharged.
2. Load test (cold start test)
For the load test, you need a special device that simulates the engine starting process and measures how well the battery withstands load.
- Connect test device: Connect the load test device to the battery, similar to the multimeter.
- Run the test: Follow the device instructions to start the test. The device draws a high current for a short period of time to simulate the load of starting the engine.
- Evaluate results: The device gives you a result that shows whether the battery can deliver the required starting power.
3. Check with a battery tester
Modern battery testers can provide a detailed analysis of battery health, including charge capacity, internal resistance and possible defects.
- Connect tester: Connect the battery tester to the battery according to the instructions.
- Carry out a test: Start the test process on the device, which can run automatically depending on the model.
- Interpret results: The tester provides a report on the condition of the battery, including recommendations as to whether the battery is still good, should be charged, or replaced.
General tips
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the battery for obvious damage, corrosion at the terminals, or battery acid leakage.
- Cleaning the connectors: Corroded or dirty connectors can result in poor electrical connections and affect performance.
- Maintenance-free battery: With maintenance-free batteries, you can often estimate the charge level using a built-in indicator.
Through these tests, you can make an informed decision about whether your car battery is still healthy or whether it is time for maintenance or replacement.
How do you measure the quiescent current and find silent consumers in the vehicle?
To measure the quiescent current and find silent consumers in a vehicle, follow these steps:
Needed tools:
- A digital multimeter capable of measuring small currents (in milliamperes).
1. Preparing for measurement
- Turn off all consumers: Make sure all electrical devices such as lights, radio, air conditioning, etc. are turned off.
- Turn off the vehicle: Turn off the vehicle completely and remove the key from the ignition.
- Waiting time: After turning off the vehicle, wait approximately 15-30 minutes to allow all electronic systems to enter sleep mode.
2. Set the measuring device
- Multimeter: Set your digital multimeter to the current measurement range (amps). Choose a suitable measuring range that can measure small currents (in the milliampere range).
3. Connecting the multimeter
- Disconnect the negative battery cable: Carefully disconnect the negative (black) battery cable from the battery.
- Connecting the multimeter: Connect the black measuring cable of the multimeter to the negative battery terminal and the red cable to the disconnected negative battery cable. The multimeter is now connected in series with the circuit and can measure the quiescent current.
4. Measuring the quiescent current
- Read the current value: A normal quiescent current value is typically between 20 and 50 milliamperes (mA). Values that are significantly higher indicate a silent consumer.
5. Identifying silent consumers
A battery monitor or voltage meter from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Remove fuses one at a time: Begin removing one fuse at a time while observing the current reading on the multimeter. A significant drop in quiescent current after removing a particular fuse indicates that the circuit to which the fuse belongs contains a silent load.
- Check associated components: After the circuit in question has been identified, check all components connected to that circuit to find the exact load.
Tips
- Patience is important: It can take some time to identify the exact silent load, especially in complex electrical systems.
- Using a memory saver: To prevent losing settings such as the time or radio stations, a memory saver can be useful while the battery is disconnected.
- Professional help: If you have difficulty finding the silent consumer or are unsure about how to take the measurement, consider consulting a professional.
This method will help you measure the quiescent current and identify silent loads that may contribute to battery discharge.
How do I check the battery voltage of a car battery with a battery tester?
To check the battery voltage of a car battery with a battery tester, follow these basic steps. Battery testers can range from simple voltmeters to complex devices that provide additional information such as cold cranking current (CCA) and battery health. The instructions focus on a basic battery voltage test:
Needed tools:
- Battery tester: This can be a simple voltmeter or a specialized car battery tester.
Steps to check battery voltage:
1. Preparation:
Make sure the vehicle and all electronic devices are turned off to ensure an accurate measurement.
2. Set battery tester:
If your battery tester has different modes, set it to measure direct voltage (DC). The setting should be higher than the expected battery voltage, usually 20V on most digital multimeters when this feature is available.
3. Tester connection:
Connect the positive (red) cable of the battery tester to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
Connect the negative (black) cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
4. Reading the voltage:
Read the voltage on the battery tester display. A healthy, fully charged car battery should read about 12.6 volts. Values below this can indicate a need for charging or wear on the battery.
Interpretation of the results:
- 12.6 volts or higher: The battery is fully charged.
- 12.4 volts: The battery is 75% charged.
- 12.2 volts: The battery is 50% charged.
- Below 12 volts: The battery is weak and may need to be charged or replaced.
Additional tips:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Testing under load: Some battery testers can test the battery under load to evaluate how well the battery can provide starting current. This is particularly useful for assessing battery performance at low temperatures.
- Testing the charging system: In addition to checking the battery, it may be useful to test the vehicle's charging system (alternator) to ensure that the battery is being charged correctly while driving.
By regularly checking the battery voltage and general health of your car battery, you can ensure that your vehicle starts reliably and avoid unexpectedly stalling with a dead battery.
My car battery keeps discharging - what action can I take?
A constantly draining car battery can be frustrating and is often a sign of an underlying problem. Here are some steps you can take to determine the cause and resolve the issue:
1. Check the battery and connections
- Clean the battery terminals: Corrosion on the battery terminals can lead to poor electrical connections. Clean the terminals with a brush and a solution of baking soda and water.
- Check connections: Make sure connections are tight and not corroded.
2. Check for parasitic power consumption
A battery monitor or voltage meter from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Test Parasitic Discharge: Some electrical devices may continue to use power even when the vehicle is turned off. Disconnect the negative battery terminal and use a multimeter to measure the current between the battery terminal and the battery post. A value above 50 mA may indicate a problem.
- Identify the power guzzler: Pull fuses one at a time to identify the system that is consuming the power. Once the power consumption drops when a particular fuse is pulled, you have found the problematic system.
3. Check the charging system
- Check the Alternator: A faulty alternator cannot charge the battery properly. Check the voltage on the battery while the engine is running; it should be between 13.7 and 14.7 volts.
4. Check the battery itself
- Carry out a battery test: A defective or old battery cannot hold the charge. Have the battery tested at a repair shop to determine if it needs to be replaced.
- Consider battery age: Car batteries have a limited lifespan, typically 3-5 years. If your battery is older, it might be time for a replacement.
5. Check for electrical shorts
- Check for Short Circuits: An electrical short circuit can drain the battery overnight. This can be a difficult task and may require diagnosis by a professional.
6. Rethink usage behavior
- Adjust driving behavior: Short journeys are often not enough to fully charge the battery. Try driving longer distances or using a battery charger for longer periods of idle time.
7. Use a trickle charger
- Connect a trickle charger: If your vehicle will not be used for a long period of time, a trickle charger can help keep the battery fully charged without overcharging it.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, it may be helpful to seek professional help. A professional can perform a more thorough diagnosis to determine the cause of the battery discharge.
How do I check the battery voltage of a vehicle battery with a multimeter?
To check the battery voltage of a vehicle battery with a multimeter, follow these steps. This guide will help you quickly and safely measure the voltage of your car battery to assess its condition.
Needed tools:
- Digital multimeter: Make sure it can be set to measure direct voltage (DC).
Steps to check battery voltage:
1. Make sure the vehicle is turned off:
Turn off the vehicle and all electronic devices to ensure an accurate measurement.
2. Setting the multimeter:
Set the multimeter to the direct voltage (DC) setting. This is usually marked by a symbol that resembles a solid line with three dashed lines underneath. Choose a measuring range that is higher than the expected voltage of the battery - for a car battery, a range of 20V is ideal.
3. Multimeter connection:
Connect the red test lead (positive) of the multimeter to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
Connect the black measuring cable (negative) to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
4. Reading the voltage:
Read the value on the multimeter. A healthy, fully charged car battery should read about 12.6 volts at rest. Values below this range may indicate that the battery needs charging or may be defective.
Interpretation of the results:
- 12.6 volts or more: The battery is fully charged.
- Between 12.4 and 12.6 volts: The battery is partially charged.
- Below 12.4 volts: The battery is weak and probably needs to be charged.
- Below 12.0 volts: The battery is discharged and may not function properly.
More information:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Test voltage under load: For a more thorough check, you can also measure the voltage of the battery under load by starting the engine or turning on the headlights. A significant drop in voltage may indicate a weak battery.
- Check the charging system: It is also a good idea to check the vehicle's charging system by measuring the voltage of the battery while the engine is running. A voltage between 13.7 and 14.7 volts indicates that the charging system is working correctly.
By regularly checking the battery voltage, you can effectively monitor the health of your vehicle battery and ensure that your vehicle starts reliably.
What should you pay attention to when measuring the 24 volt voltage of the truck starter battery?
When measuring the voltage of a 24 volt starter battery/vehicle battery, such as those often found in commercial vehicles, buses or large trucks, there are a few specific points to consider in order to achieve accurate and safe results:
1. Using a suitable multimeter
Make sure your multimeter is rated for measurements up to 24 volts or higher. Most digital multimeters can easily measure these voltages, but it's always good to check the specifications before measuring.
2. Correct setting of the multimeter
Select the direct voltage (DC) setting on the multimeter. On most multimeters this is represented by the "V" symbol with a straight line (and possibly a dashed line for AC voltage). Set the multimeter to a measurement range that is above 24 volts.
3. Safety precautions
- Disconnect all consumers: Make sure all consumers in the vehicle (e.g. lights, radio) are turned off to get an accurate measurement.
- Avoiding short circuits: Make sure that the measuring tips of the multimeter do not touch metal parts of the vehicle at the same time and thus cause a short circuit.
- Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing as necessary, especially when working with larger battery banks, to protect yourself from acid and electrical shock.
4. Measurement of voltage
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
- Pay attention to polarity: Connect the red measuring cable of the multimeter to the positive (+) pole and the black measuring cable to the negative (−) pole of the battery.
- Measure total battery voltage: A 24-volt battery is often two 12-volt batteries connected in series. Make sure you measure the voltage across the entire battery bank to capture the total voltage of 24 volts.
5. Interpretation of the measured values
- A fully charged 24-volt battery should have a resting voltage of approximately 25.2 to 25.8 volts.
- Voltages below 24 volts may indicate a discharge or a problem with one of the batteries in the series.
- Note that an accurate assessment of battery health should not be based on voltage alone. A capacity test or under load test may be required to evaluate the actual condition of the battery.
6. Check both batteries
If you have access to the individual 12-volt batteries connected in series, it may make sense to check each battery individually to ensure that both are evenly charged and functioning properly. Differences in voltage between the two batteries can indicate problems.
By paying attention to these points, you will ensure that you can take an accurate and safe voltage measurement on a 24-volt starter battery.
How do I check a car battery, better with a multimeter or battery tester? Answer with advantages and disadvantages to the question.
Testing a car battery can be done using both a multimeter and a special battery tester. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the tools available, your needs, and the depth of analysis you want.
multimeter
Advantages:
- Universal use: A multimeter can be used for a variety of electrical measurements, not just car batteries.
- Cost-effective: Many people already own a multimeter, and it is cheaper than a specialized battery tester.
- Easy voltage measurement: It allows quick and easy measurement of battery voltage to get a rough overview of the charge status.
Disadvantages:
- Limited information: A multimeter can only measure voltage. There is no direct information about the cold cranking performance (CCA) or overall health of the battery.
- Requires Interpretation: Results require some interpretation and without experience it may be difficult to interpret correctly.
Battery tester
Advantages:
- Specific analyses: In addition to voltage, a battery tester can also measure cold cranking performance, internal resistance and sometimes capacity. These tests provide a more complete picture of the battery's health.
- Easy to interpret: Many battery testers report results in an easy-to-understand form, often with a direct assessment of battery health.
- Fast and comprehensive diagnosis: You are able to quickly create a comprehensive diagnosis that goes beyond just measuring voltage.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: Battery testers can be more expensive than multimeters, especially if they offer advanced features.
- Specialization: They are specifically designed for battery testing and are not as versatile as multimeters.
Conclusion
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
If you already own a multimeter and just want to do a quick voltage check or are on a budget, this is a viable option. A multimeter can provide a good initial check to see if the battery may be dead or defective.
For a deeper analysis, especially if you are in car repair or maintenance or want a more detailed assessment of battery health, a specialized battery tester is a better choice. It provides more detailed information that can be essential for maintenance and troubleshooting.
In practice, both tools complement each other well. A multimeter for quick checks and basic measurements, and a battery tester for detailed analysis and to comprehensively assess the battery's health.

What happens if you install a more powerful vehicle battery?
Installing a more powerful vehicle battery, that is, a battery with a higher capacity (measured in Ampere Hours, Ah) or higher cold cranking capacity (measured in Cold Cranking Amps, CCA), can have various effects on the vehicle. In most cases, this will have positive effects as long as the battery physically fits into the intended battery space and the electrical specifications (such as voltage) are compatible with the vehicle system.
Monitoring battery voltage with a HOOTS battery sensor:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
Here are some of the possible impacts:
Positive impact:
- Longer lifespan: A higher capacity battery can provide power for longer before needing to be recharged. This is particularly useful in situations where many electrical consumers are used in the car or the vehicle is often driven for short distances, which does not always give the battery the opportunity to fully recharge.
- Better Cold Weather Performance: A battery with higher cold cranking amps (CCA) can help the engine start more easily in cold weather. This is particularly beneficial in colder climates where low temperatures can affect battery performance.
- Reliability: A stronger battery can be more reliable overall because it is less likely to go into a deep discharge state under normal circumstances.
Possible concerns:
- Physical Size: A larger battery may not fit in the vehicle's battery compartment. It is important to ensure that the dimensions and mounting points are compatible.
- Charging System Compatibility: The vehicle charger (typically the alternator) should be able to effectively charge the larger battery. Modern alternators are typically designed to handle a wide range of battery sizes, but on older vehicles this could be a problem.
- Cost: Larger batteries are generally more expensive. It is important to weigh the costs against the benefits.
- Excessive Capacity: While larger capacity provides benefits, an excessively large battery may not provide additional benefits to the vehicle and is merely an unnecessary expense.
Summary:
Upgrading to a more powerful vehicle battery can improve vehicle reliability and performance, especially in demanding conditions. However, it is important to consider compatibility, cost and actual needs. As long as the new battery physically fits, is the correct voltage, and the vehicle charger is appropriate, the stronger battery should have no negative impact on the vehicle.
What happens if you install a more powerful vehicle battery?
Installing a more powerful vehicle battery, that is, a battery with a higher capacity (measured in Ampere Hours, Ah) or higher cold cranking capacity (measured in Cold Cranking Amps, CCA), can have various effects on the vehicle. In most cases, this will have positive effects as long as the battery physically fits into the intended battery space and the electrical specifications (such as voltage) are compatible with the vehicle system.
Monitoring battery voltage with a HOOTS battery sensor:
A battery monitor from HOOTS, controlled via an app and software, enables detailed and user-friendly monitoring of battery systems and chargers.
Here are some of the possible impacts:
Positive impact:
- Longer lifespan: A higher capacity battery can provide power for longer before needing to be recharged. This is particularly useful in situations where many electrical consumers are used in the car or the vehicle is often driven for short distances, which does not always give the battery the opportunity to fully recharge.
- Better Cold Weather Performance: A battery with higher cold cranking amps (CCA) can help the engine start more easily in cold weather. This is particularly beneficial in colder climates where low temperatures can affect battery performance.
- Reliability: A stronger battery can be more reliable overall because it is less likely to go into a deep discharge state under normal circumstances.
Possible concerns:
- Physical Size: A larger battery may not fit in the vehicle's battery compartment. It is important to ensure that the dimensions and mounting points are compatible.
- Charging System Compatibility: The vehicle charger (typically the alternator) should be able to effectively charge the larger battery. Modern alternators are typically designed to handle a wide range of battery sizes, but on older vehicles this could be a problem.
- Cost: Larger batteries are generally more expensive. It is important to weigh the costs against the benefits.
- Excessive Capacity: While larger capacity provides benefits, an excessively large battery may not provide additional benefits to the vehicle and is merely an unnecessary expense.
Summary:
Upgrading to a more powerful vehicle battery can improve vehicle reliability and performance, especially in demanding conditions. However, it is important to consider compatibility, cost and actual needs. As long as the new battery physically fits, is the correct voltage, and the vehicle charger is appropriate, the stronger battery should have no negative impact on the vehicle.


